How Do You Fix Receding Gums?
Gum health often doesn’t get as much attention as it should, until something feels off. Receding gums can start slowly, showing up as mild sensitivity or slight changes in how your teeth look. But left unaddressed, the issue can lead to more serious problems like exposed roots or gum infections.
In Singapore, gum-related concerns are more common than many realise. A 2019 poll involving 1,196 adults found that 90% had some form of gum disease. And gum recession is often one of the early signs.
This makes it all the more important to understand what causes gums to recede and what you can do to manage the condition before it worsens.
Understanding Gum Recession
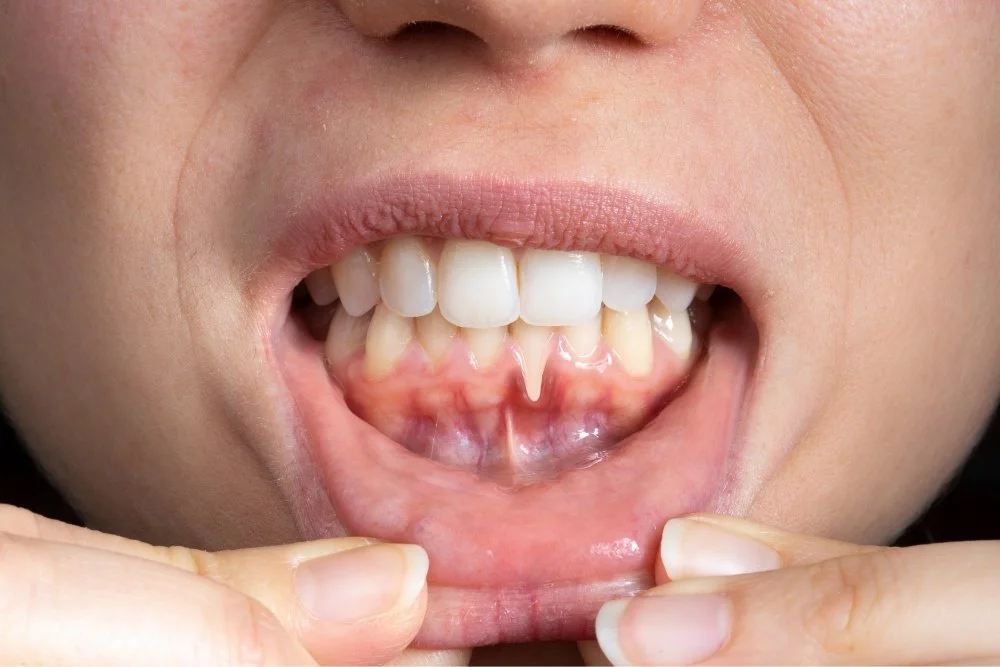
Gingival recession, referred to as gum recession, describes the condition where the gum tissue that supports your teeth starts to pull away or wear down. This slow process gradually exposes more of the tooth surface and, in some cases, the root. Because it tends to progress over time, many people may not notice it until sensitivity kicks in or their teeth begin to look longer.
Beyond appearance, receding gums can affect how your mouth functions. Gaps may form between the gum and tooth, creating areas where bacteria can collect and cause further damage. If left unaddressed, this can lead to deeper oral health issues that affect both the gums and supporting bone.
Recognising the Signs of Gum Recession
As mentioned, gum recession tends to happen gradually, which means you might not realise something is wrong until it becomes more obvious. Some of the early signs you might notice include:
Increased tooth sensitivity: You may feel a sharp or lingering discomfort when consuming hot, cold, or sweet items. This usually points to exposed roots, which lack the protective enamel found on the crown of the tooth.
Teeth appearing longer: A subtle but common sign is noticing that your teeth seem to be “growing.” But what’s actually happening is the gum tissue pulling away, revealing more of the tooth’s surface.
Visible root exposure: If you spot a yellowish or darker section near the base of your tooth, it’s likely the root. This is a key indicator that gum tissue has worn down significantly.
Gaps or pockets forming: Receding gums can create small spaces between the tooth and gum. These pockets can trap food or bacteria, making it harder to maintain good oral hygiene.
Key Factors That Cause Gums to Recede
So, what causes the gum tissue to start pulling back in the first place?
While gum recession can affect anyone, there are several factors that tend to play a bigger role than others:
Periodontal disease: Chronic inflammation caused by gingivitis or periodontitis is one of the most common contributors. As the infection progresses, it breaks down gum tissue and supporting bone, leading to visible recession.
Brushing too hard: This might come as a surprise for some, but using a toothbrush with stiff bristles or brushing with too much pressure can wear away the gum margin over time.
Poor oral hygiene: Skipping regular brushing or flossing can allow plaque to build up. Over time, this hardens into tartar and creates the right environment for gum inflammation and damage.
Tobacco use: Smoking or chewing tobacco irritates the gums and restricts blood flow, making it harder for the tissue to stay healthy and intact.
Hormonal changes: Fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, or menstruation can affect gum sensitivity and increase the risk of recession, especially when oral hygiene isn’t consistent.
Teeth grinding (bruxism): Constant grinding or clenching puts stress on the gum line and supporting structures, which can contribute to gum recession.
Genetics: Some people naturally have thinner gum tissue or are more prone to recession, even with good hygiene.
Misaligned bite: When teeth don’t meet properly, the uneven force distribution can cause gum irritation or wear in specific areas.
Why Gum Recession Can Harm Oral Health
It’s common for people to delay dental visits when symptoms seem mild or painless, but ignoring gum recession may result in various dental complications that often worsen over time.
Tooth sensitivity: One of the first things people notice is discomfort when consuming hot, cold, or sweet food. This happens because the exposed root lacks enamel protection.
Tooth decay: Unlike enamel, root surfaces are more prone to decay. Once exposed, they can wear down faster, increasing the risk of cavities near the gum line.
Progressing gum disease: Gum recession doesn’t happen in isolation. It often signals ongoing inflammation, and without intervention, the disease can spread deeper into the gum and bone structures.
Loose teeth: As the gums pull away and support weakens, some teeth may begin to shift or feel loose. This affects both chewing and long-term stability.
Aesthetic changes: Receding gums can change the shape of your smile. Some teeth may appear longer than others, or gaps may become more noticeable, which can affect facial balance.
Can Receding Gums Grow Back?
While gum recession may start off subtle, its effects can be lasting. One obvious repercussion is the fact that once gum tissue recedes, it doesn’t regenerate naturally. The loss is permanent, but that doesn’t mean nothing can be done. With the right steps, you can stop the gum recession from getting worse and protect what remains.
What’s most important is early detection. The earlier you act, the more options you have to manage your condition and learn how to prevent gum recession in future.
Early-Stage Dental Treatments for Receding Gums
Still worried about gum recession getting worse?
In mild cases, non-surgical options may be enough to control the issue. One approach is routine scaling and root planing, a deep-cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar buildup below the gumline. This can help reduce inflammation and lowers the risk of gum detachment.
Orthodontic treatments like dental braces or Invisaligns can also help. If your gum recession stems from a misaligned bite, adjusting tooth positions may reduce uneven pressure on the gums.
In more serious cases, professional gum recession treatment may be necessary. This could involve deep cleaning, scaling and root planing, or procedures like gum grafting to restore coverage and reduce sensitivity.
Daily habits matter too. Making small but consistent changes like switching to a soft-bristled toothbrush and brushing more gently can play a key role in stopping receding gums from getting worse.
Other Treatment Options for Severe Gum Recession
However, if the gum loss has already progressed, you may need more intensive procedures to protect your teeth and manage sensitivity.
A surgical approach for addressing gum recession is gum grafting, which involves transplanting tissue from another area of the patient's mouth or from a suitable donor source. This graft is then carefully positioned to cover the exposed root surfaces. This helps rebuild the gumline and shield the roots from further exposure.
Another technique is the Pinhole Surgical Technique (PST). Instead of sutures, this method uses a tiny opening to loosen and reposition existing gum tissue, offering a less invasive alternative for certain cases.
These options are usually recommended for advanced gum recession where brushing habits or deep cleaning alone won’t be enough to restore coverage.
At-Home Strategies to Support Gum Health
Alongside dental visits, simple adjustments to your daily routine can help protect your gums from further damage.
Start with gentle brushing. A soft-bristle toothbrush and light pressure are key to preventing irritation. In addition, be sure to floss daily to remove plaque that your toothbrush can’t reach, and rinse with an alcohol-free mouthwash.
Using desensitising toothpaste may also help if you’re dealing with discomfort from exposed roots. These formulas are designed to ease sensitivity and support enamel protection.
However, do note that these steps do not replace professional care such as dental scaling and polishing, but every step adds up when you're trying to maintain your gum health between appointments.
Lifestyle Changes That Support Healthier Gums
Daily care matters, but your overall lifestyle plays a big part in how your gums hold up over time. These lifestyle changes can offer additional protection:
Quit smoking: Reduces gum irritation, improves blood flow, and supports immune function.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: Focus on antioxidant-rich foods to help with tissue repair and inflammation control.
Stay hydrated: Saliva plays a key role in protecting your gums and washing away harmful bacteria.
Wear a mouthguard if needed: Prevents damage from teeth grinding or clenching, especially during sleep.
Visit your dentist regularly: Allows for early diagnosis, ongoing monitoring, and professional cleanings to prevent further recession.
These adjustments may seem simple, but they add up, and can make a real difference in keeping your gums healthier over time.
If you're concerned about your gums pulling back or exposing your teeth, early action matters. The best way to stop the recession from worsening is by combining daily care with professional dental services tailored to your needs. At Sincere Dental, we provide practical support to help you protect what remains and manage your oral health long-term.
Book a consultation today to find out how we can support you.